Cholesterol is a crucial component of the body, serving various physiological functions. However, maintaining an optimal cholesterol ratio is imperative for heart health. The cholesterol ratio, which compares the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, is a key indicator of cardiovascular risk. A higher ratio of HDL to LDL cholesterol is associated with a lower risk of heart disease, as HDL cholesterol helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream, preventing the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
Monitoring and managing cholesterol levels, particularly the ratio between HDL and LDL cholesterol, is essential for reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco use, can help improve cholesterol levels and promote cardiovascular health. Additionally, medications may be prescribed to lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve the cholesterol ratio in individuals at higher risk of heart disease. By understanding the significance of cholesterol ratio and implementing strategies to maintain a healthy ratio, individuals can reduce their risk of cardiovascular events and lead healthier lives.
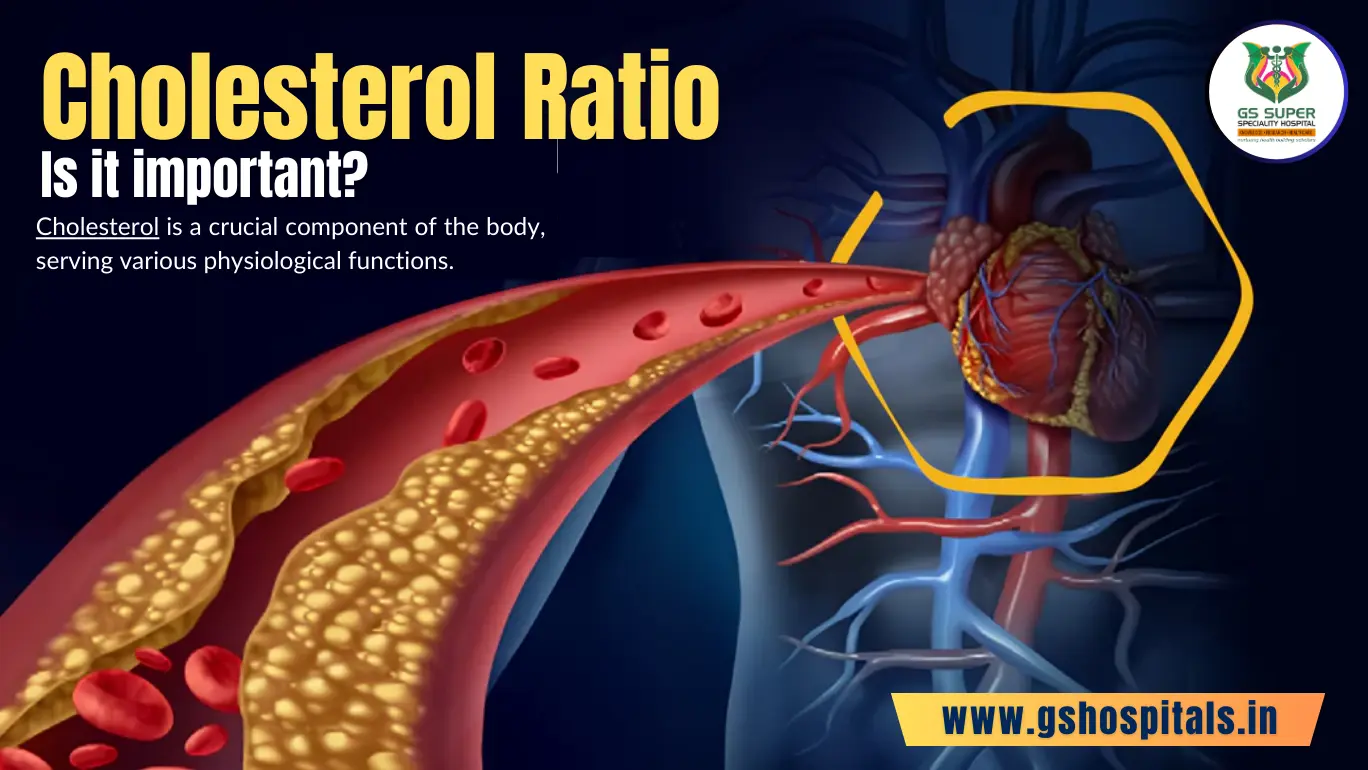
The cholesterol ratio is a crucial metric that provides insights into the balance between different types of cholesterol present in the bloodstream. It serves as a valuable indicator of cardiovascular health, with higher levels of HDL cholesterol considered beneficial and lower levels of LDL cholesterol indicative of potential risk factors for heart disease.
The cholesterol ratio is significant because it reflects the relative proportions of HDL and LDL cholesterol in the blood. HDL cholesterol acts as a scavenger, transporting excess cholesterol from the bloodstream to the liver for processing and removal. In contrast, LDL cholesterol can accumulate in the arteries, leading to plaque buildup and increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
To calculate the cholesterol ratio, one divides the total cholesterol level by the HDL cholesterol level. For instance, if an individual's total cholesterol is 200 mg/dL and their HDL cholesterol is 50 mg/dL, the cholesterol ratio would be 4:1. A lower ratio indicates a healthier balance, with higher levels of protective HDL cholesterol relative to LDL cholesterol.
Ideally, individuals should aim for a cholesterol ratio below 5:1, with values closer to 3.5:1 or lower considered optimal for heart health. A higher ratio may indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, while a lower ratio suggests a reduced risk.
Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels, including the cholesterol ratio, is essential for assessing cardiovascular risk and guiding preventive measures. Lifestyle modifications such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking can help improve cholesterol levels and promote overall heart health. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to further lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve the cholesterol ratio.
Understanding and monitoring the cholesterol ratio is vital for maintaining cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. By striving for a favorable cholesterol ratio through lifestyle modifications and appropriate medical interventions, individuals can take proactive steps towards safeguarding their heart health and overall well-being.
The cholesterol ratio plays a crucial role in evaluating cardiovascular risk by providing insights into the balance between HDL and LDL cholesterol levels in the bloodstream. A higher ratio indicates an elevated risk of developing cardiovascular disease, as it suggests an imbalance with higher levels of LDL cholesterol, which can contribute to arterial plaque buildup and increase the likelihood of heart-related complications. Conversely, a lower ratio signifies better heart health, with higher levels of protective HDL cholesterol helping to mitigate cardiovascular risk factors.
Regular monitoring of the cholesterol ratio enables healthcare providers to predict future health risks and implement preventive measures accordingly. By tracking changes in the ratio over time, clinicians can identify individuals at higher risk of developing heart disease or stroke and intervene with lifestyle modifications or medical interventions to mitigate these risks. Additionally, the cholesterol ratio serves as an early warning sign of potential cardiovascular problems, allowing for timely interventions and personalized treatment strategies to improve overall heart health and reduce the likelihood of adverse cardiovascular events.
The ideal cholesterol ratio is typically defined as less than 4:1, indicating a balance between HDL and LDL cholesterol levels conducive to good cardiovascular health. However, ratios lower than 3.5:1 or even 3:1 are associated with even better cardiovascular outcomes, highlighting the importance of achieving optimal lipid balance for heart health.
Cholesterol ratios serve as valuable indicators of cardiovascular risk, with ratios above 5:1 signaling an increased likelihood of heart disease. Conversely, ratios below 3.5:1 are considered optimal and indicative of lower cardiovascular risk. Individuals falling within the range of 4:1 to 5:1 may benefit from lifestyle modifications aimed at improving their cholesterol ratio, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing other risk factors like hypertension and obesity. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels and ratios can help individuals and healthcare providers assess cardiovascular risk and tailor interventions accordingly to promote heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Lifestyle choices significantly impact cholesterol levels and, consequently, the cholesterol ratio.
Diet: Consuming a diet rich in saturated and trans fats, commonly found in processed foods, red meat, and full-fat dairy products, can elevate LDL cholesterol levels while lowering HDL cholesterol levels, leading to an unfavorable cholesterol ratio.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise plays a pivotal role in maintaining optimal cholesterol levels and improving the cholesterol ratio. Physical activity boosts HDL cholesterol levels, the "good" cholesterol, which helps offset the adverse effects of LDL cholesterol.
Genetic predispositions can influence cholesterol levels and, subsequently, the cholesterol ratio.
Family History: Individuals with a family history of high cholesterol or heart disease may have a genetic predisposition to unfavorable cholesterol ratios. Genetic factors can impact how the body processes cholesterol and regulates lipid levels, contributing to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Certain medical conditions can disrupt cholesterol metabolism and affect the cholesterol ratio.
Metabolic Disorders: Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome can adversely affect cholesterol levels, leading to an imbalance between LDL and HDL cholesterol and an unfavorable cholesterol ratio.
Medications: Some medications, including statins and cholesterol-lowering drugs, can help manage cholesterol levels and optimize the cholesterol ratio. These medications work by inhibiting cholesterol synthesis or enhancing its clearance from the bloodstream, thereby improving lipid profiles and reducing cardiovascular risk.
Understanding the various factors influencing cholesterol ratio is crucial for implementing targeted interventions aimed at optimizing lipid levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Lifestyle modifications, genetic predispositions, and underlying medical conditions all play integral roles in determining an individual's cholesterol profile and overall cardiovascular health. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels, coupled with appropriate lifestyle changes and medical interventions, can help individuals achieve and maintain a favorable cholesterol ratio for long-term heart health.
A balanced and nutritious diet is fundamental for managing cholesterol levels and optimizing the cholesterol ratio.
Consume Whole Foods: Incorporate a variety of whole foods into your diet, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (such as poultry, fish, beans, and legumes), and healthy fats (such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil).
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: Minimize the intake of foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as processed snacks, fried foods, fatty meats, and full-fat dairy products. These fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
Physical activity plays a pivotal role in maintaining heart health and promoting a favorable cholesterol ratio.
Engage in Aerobic Exercise: Participate in regular aerobic activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming to elevate HDL cholesterol levels and lower LDL cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Incorporate Strength Training: Include strength training exercises in your fitness routine to build muscle mass and improve overall metabolic health. Strength training can complement aerobic exercise in managing cholesterol levels and optimizing the cholesterol ratio.
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for managing cholesterol levels and reducing cardiovascular risk.
Adopt a Balanced Approach: Focus on achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Aim for a body mass index (BMI) within the normal range (18.5 to 24.9 kg/m²).
Monitor Portion Sizes: Be mindful of portion sizes and practice portion control to prevent overeating and unnecessary calorie consumption. Incorporate mindful eating practices such as chewing slowly and savoring each bite to promote satiety and prevent overindulgence.
Smoking has detrimental effects on cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health.
Quit Smoking: Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful steps you can take to improve your cholesterol ratio and reduce the risk of heart disease. Smoking not only lowers HDL cholesterol levels but also damages the lining of the arteries, promotes inflammation, and increases the risk of atherosclerosis and heart attacks.
Seek Support: Seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or smoking cessation programs to quit smoking successfully. Utilize nicotine replacement therapy, medications, counseling, or other evidence-based strategies to overcome nicotine addiction and maintain long-term abstinence.
Implementing these lifestyle strategies can help maintain a healthy cholesterol ratio, reduce cardiovascular risk, and promote overall heart health. Consistency and commitment to these habits are key to achieving lasting benefits and optimizing your cholesterol profile for a healthier life.
Best Heart Care Centre in Ghaziabad at GS Hospital, we offer comprehensive cholesterol screening and management services, including lipid profile testing, lifestyle counseling, and medication management to optimize cholesterol levels and reduce cardiovascular risk.
GS Hospital provides patient education programs and resources to raise awareness about the importance of cholesterol management, healthy lifestyle habits, and preventive measures for heart disease.
Yes, one of the Top Heart Care Hospital in UP GS Hospital offers specialized cardiac care services, including cardiology consultations, diagnostic testing, and treatment options tailored to patients with high cholesterol and cardiovascular risk.
Patients can schedule a cholesterol screening or consultation with a cardiologist at the best Hospital in Ghaziabad at GS Hospital by contacting our cardiology department or scheduling an appointment through our website or phone line. We prioritize timely access to care and personalized treatment plans for all patients.
Absolutely, GS Hospital provides support and resources for patients looking to make lifestyle changes to improve their cholesterol ratio, including dietary guidance, exercise programs, smoking cessation support, and access to nutritionists and wellness experts. We believe in empowering patients to take control of their heart health and achieve optimal outcomes.