Did you know the symptoms of Skin Cancer & how it is caused?
Published On : July 05, 2024
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, yet many people are unaware of its symptoms and causes. Early detection and understanding how to prevent it are crucial for effective treatment and better outcomes. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms of skin cancer, its causes, and the expert care available at GS Hospital, one of the best cancer hospital in Ghaziabad and Meerut.
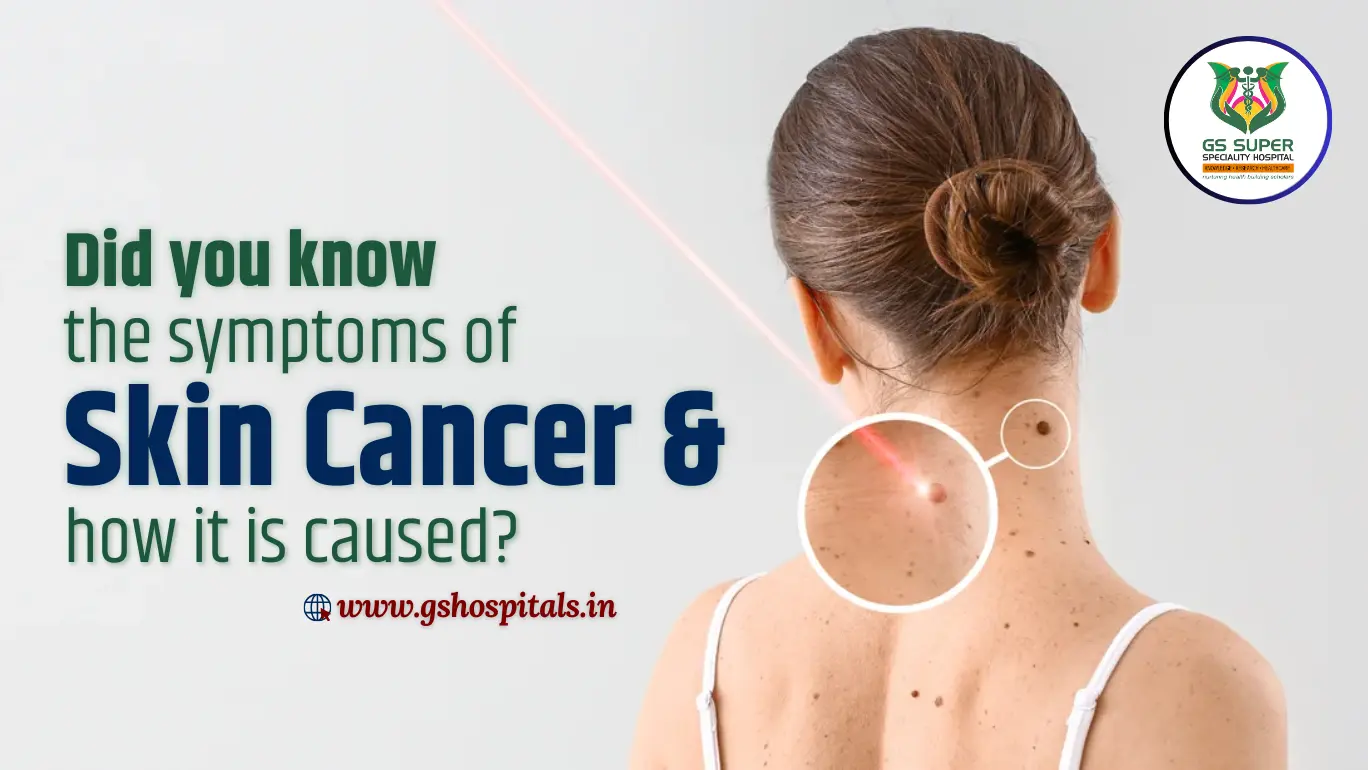
Importance of Awareness about Skin Cancer:
Skin cancer, though common, can be life-threatening if not detected and treated early. Raising awareness about its symptoms and causes is crucial for early diagnosis and improving survival rates. Key aspects of skin cancer awareness include:
- Understanding Risk Factors: Knowing that factors such as excessive sun exposure, use of tanning beds, family history, and fair skin increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
- Recognizing Symptoms: Early signs of skin cancer can include new or changing moles, unusual skin growths, sores that don’t heal, and changes in skin texture or color. Awareness campaigns can help people recognize these symptoms early.
- Promoting Regular Skin Checks: Encouraging regular self-examinations and dermatological check-ups to catch any suspicious changes in the skin promptly.
Role of GS Hospital in Cancer Treatment:
Best Cancer Hospital in Meerut like GS Hospital is renowned for its comprehensive cancer care, offering advanced treatment facilities and a multidisciplinary approach to patient care. The hospital's contributions include:
Expertise of Oncologists:
- Top Oncologists: GS Hospital features some of the best oncologists in Hapur, who specialize in diagnosing and treating various forms of cancer, including skin cancer.
- Multidisciplinary Teams: The hospital employs a team-based approach, involving oncologists, dermatologists, radiologists, and surgeons to provide holistic care for cancer patients.
Advanced Treatment Facilities:
- Cutting-Edge Technology: GS Hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment equipment, ensuring accurate detection and effective treatment of skin cancer.
- Comprehensive Care: From radiation therapy and chemotherapy to surgical interventions and immunotherapy, GS Hospital offers a wide range of treatment options tailored to the specific needs of each patient.
Support Services:
- Patient Education: GS Hospital provides educational resources and counseling to help patients understand their condition and treatment options.
- Support Groups: The hospital facilitates support groups for patients and their families, providing emotional support and sharing experiences to help cope with the challenges of cancer treatment.
Understanding Skin Cancer:
What is Skin Cancer?:
Skin cancer occurs when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably. It primarily develops on skin exposed to the sun, but it can also occur in areas not ordinarily exposed. Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer, and early detection is critical for effective treatment.
Types of Skin Cancer:
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC):
- Overview: BCC is the most common type of skin cancer, originating in the basal cells, which produce new skin cells as old ones die off.
- Appearance: BCC often appears as a slightly transparent bump on the skin, but it can also manifest as a flat, flesh-colored or brown scar-like lesion.
- Risk Factors: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds significantly increases the risk of BCC.
- Treatment: Treatment options include surgical excision, Mohs surgery, cryotherapy, and topical medications.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC):
- Overview: SCC develops in the squamous cells that make up the middle and outer layers of the skin. It is more aggressive than BCC and can spread to other parts of the body if not treated promptly.
- Appearance: SCC may present as a red nodule, a flat sore with a scaly crust, or a new sore or raised area on an old scar or ulcer.
- Risk Factors: SCC is also linked to UV radiation exposure, as well as factors like a history of precancerous skin lesions, fair skin, and chronic skin inflammation.
- Treatment: Treatments include surgical removal, radiation therapy, cryotherapy, and photodynamic therapy.
Melanoma:
- Overview: Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer. It develops in the melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, which gives skin its color.
- Appearance: Melanoma can form in existing moles or suddenly appear as a new dark spot on the skin. It is often characterized by asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colors, and a diameter larger than 6mm.
- Risk Factors: Risk factors include severe, blistering sunburns, excessive UV radiation exposure, having many moles or atypical moles, and a family history of melanoma.
- Treatment: Treatment options range from surgical excision and immunotherapy to targeted therapy, radiation, and chemotherapy for advanced cases.
Preventive Measures:
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear protective clothing, and avoid peak sun hours.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular skin checks by a dermatologist and self-examinations can help detect skin cancer early.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Refrain from using tanning beds, as they increase the risk of all types of skin cancer.
Symptoms of Skin Cancer:
Common Signs to Look For:
Unusual Growths or Lumps:
- Appearance: New growths, lumps, or bumps on the skin that do not heal over time can be signs of skin cancer. These might be red, pale, or pearly in color.
- Persistence: These growths often remain despite treatments like creams or lotions and can grow over time.
- Types: These could be indicative of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or other forms of skin cancer.
Changes in Existing Moles:
- Monitoring: Changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of an existing mole should be examined by a healthcare professional.
- Symptoms: Moles that become itchy, bleed, or develop irregular edges are particularly concerning and should be checked immediately.
- Risks: Alterations in moles could signal melanoma, the most dangerous type of skin cancer.
Persistent Itching or Pain:
- Unusual Sensations: Persistent itching, tenderness, or pain in a specific area of the skin can be an indicator of skin cancer.
- Overlooked Signs: This symptom is often overlooked but should not be ignored as it can signify underlying cancerous changes.
The ABCDE Rule for Melanoma:
The ABCDE rule helps in identifying melanoma. Look for the following characteristics in moles:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other.
- Border: Edges are irregular, ragged, notched, or blurred.
- Color: The color is not uniform and may include shades of brown, black, pink, red, white, or blue.
- Diameter: The spot is larger than 6mm across (about the size of a pencil eraser), although melanomas can sometimes be smaller.
- Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
Additional Warning Signs:
- Non-Healing Sores: Sores that do not heal within a few weeks are a potential sign of skin cancer.
- Spread of Pigment: Pigment from the border of a spot into surrounding skin can be a warning sign.
- Redness or Swelling: Redness or swelling beyond the border of a mole into surrounding skin should be monitored.
- Surface Changes: Oozing, scaliness, bleeding, or the appearance of a lump or bump on the surface of the skin can indicate skin cancer.
By being vigilant about these symptoms and regularly examining your skin, you can detect skin cancer early and improve the chances of successful treatment. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are essential for maintaining skin health and catching any potential issues early.
Causes of Skin Cancer:
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation:
Sun Exposure:
- Primary Cause: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the primary cause of skin cancer.
- Mechanism: UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can cause cancer.
- Risk Areas: Areas of the skin most frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms, are at higher risk.
Tanning Beds:
- Artificial UV Sources: Tanning beds emit concentrated UV radiation, significantly increasing the risk of developing skin cancer.
- Artificial UV Sources: Tanning beds emit concentrated UV radiation, significantly increasing the risk of developing skin cancer.
- Youth Vulnerability: Young people who use tanning beds are at an especially high risk of developing skin cancer later in life.
Genetic Factors:
Family History:
- Increased Risk: A family history of skin cancer can increase an individual's risk, indicating a possible genetic predisposition to the disease.
- Inherited Traits: Certain inherited traits, such as fair skin that burns easily, can also contribute to higher risk.
Genetic Mutations:
- Susceptibility: Certain genetic mutations can increase the susceptibility to skin cancer. These mutations can be inherited or occur spontaneously.
- Specific Syndromes: Conditions like xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) are linked to higher risks due to DNA repair defects.
Environmental Factors:
Chemical Exposure:
- Hazardous Chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as arsenic, can increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
- Sources: These chemicals may be found in pesticides, herbicides, and some industrial processes.
- Occupational Risk: Workers in industries that handle such chemicals are at a higher risk.
Previous Radiation Therapy:
- Secondary Risk: Individuals who have undergone radiation therapy for other cancers have a higher risk of developing skin cancer in the treated areas.
- Cumulative Effect: The cumulative effect of radiation exposure can lead to DNA damage and subsequent skin cancer development.
Prevention and Early Detection:
Sun Protection Strategies:
Using Sunscreen:
- High SPF: Regular use of sunscreen with a high SPF can significantly reduce the risk of skin cancer.
- Application: Sunscreen should be applied generously and re-applied every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
Wearing Protective Clothing:
- Hats and Sunglasses: Wearing hats and sunglasses provides additional protection against harmful UV rays.
- Long-Sleeved Clothing: Opt for clothing with a UV protection factor (UPF) rating for better coverage.
Avoiding Tanning Beds:
- Healthier Alternatives: Steering clear of tanning beds can reduce the risk of skin cancer.
- Safe Options: Choose safer alternatives, such as self-tanning lotions or sprays, if a tanned appearance is desired.
Regular Skin Checks:
Self-Examinations:
- Routine Checks: Performing regular self-examinations can help detect skin cancer early.
- Comprehensive Inspection: Use a mirror to check all areas of the body, including the back, scalp, and soles of the feet.
Professional Screenings:
- Annual Exams: Annual skin examinations by a dermatologist are recommended, especially for those with a higher risk of skin cancer.
- Expert Analysis: Dermatologists can identify suspicious areas that may require further investigation.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnostic Procedures:
Skin Biopsy:
- Definitive Diagnosis: A skin biopsy involves removing a small sample of suspicious skin tissue for laboratory analysis.
- Accuracy: It is the most definitive way to diagnose skin cancer.
Dermatoscopy:
- Non-Invasive: Dermatoscopy uses a special magnifying lens and light source to examine skin lesions in greater detail.
- Detailed Analysis: Provides a closer look at the skin to identify potential issues.
Treatment Options:
Surgical Removal
- Common Method: Surgical removal of the cancerous tissue is the most common treatment for skin cancer.
- Variety of Techniques: This can involve simple excision, Mohs surgery, or cryosurgery, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Radiation Therapy:
- Targeted Approach: Uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells.
- Non-Surgical Option: Often used for cancers that cannot be surgically removed or in cases where surgery is not an option.
Chemotherapy:
- Drug Treatment: Involves using drugs to destroy cancer cells.
- Advanced Cases: Typically used for more advanced skin cancers or cancers that have spread to other parts of the body.
Immunotherapy:
- Immune System Boost: Helps the body's immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Melanoma Treatment: A promising treatment for advanced melanoma.
Expertise at GS Hospital:
Leading Oncologists:
- Top Specialists: GS Hospital boasts some of the best oncologists in Hapur and the surrounding regions.
- High Standard of Care: Their expertise ensures that patients receive the highest standard of care.
Advanced Treatment Facilities:
- State-of-the-Art Equipment: GS Hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities for the diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer.
- Comprehensive Services: From advanced imaging to innovative therapies, the hospital provides comprehensive care.
Personalized Patient Care:
- Individualized Plans: Best Oncologist in Ghaziabad like GS Hospital, patient care is personalized to meet the unique needs of each individual.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: The multidisciplinary team works together to develop customized treatment plans that optimize outcomes.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt attention and care. Understanding its symptoms and causes, along with regular skin checks and protective measures, can significantly reduce the risk and improve outcomes. GS Hospital, with its team of expert oncologists and advanced treatment facilities, is dedicated to providing top-notch care for skin cancer patients.
FAQs
1. What are the early signs of skin cancer?
Early signs of skin cancer include new growths, unusual lumps, changes in existing moles, and persistent itching or pain in specific areas of the skin.
2. How can I reduce my risk of developing skin cancer?
You can reduce your risk by using sunscreen regularly, wearing protective clothing, avoiding tanning beds, and performing regular skin checks.
3. What should I do if I notice a suspicious skin lesion?
If you notice a suspicious skin lesion, schedule an appointment with a dermatologist for a professional evaluation. Early detection is key to effective treatment.
4. What treatments are available for skin cancer at GS Hospital?
GS Cancer Hospital Ghaziabad like GS Hospital offers a range of treatments for skin cancer, including surgical removal, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, all provided by a team of expert oncologists.
5. How often should I have a professional skin examination?
It is recommended to have a professional skin examination annually, or more frequently if you have a higher risk of skin cancer due to factors such as family history or previous skin cancer.
