What are Ovarian Cysts: Types, Symptoms & Diagnosis Options
Published On : March 07, 2025
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form in or on the ovaries. While most ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some can cause complications, requiring medical intervention. Understanding the types, symptoms, and diagnostic options is crucial for timely treatment and peace of mind.
GS Hospital, known as the Best Hospital in Hapur, offers expert care for ovarian cysts. The hospital provides comprehensive diagnosis and treatment tailored to each patient's needs with a team of the Best Gynaecologist and Obstetrician in Ghaziabad and Meerut UP.
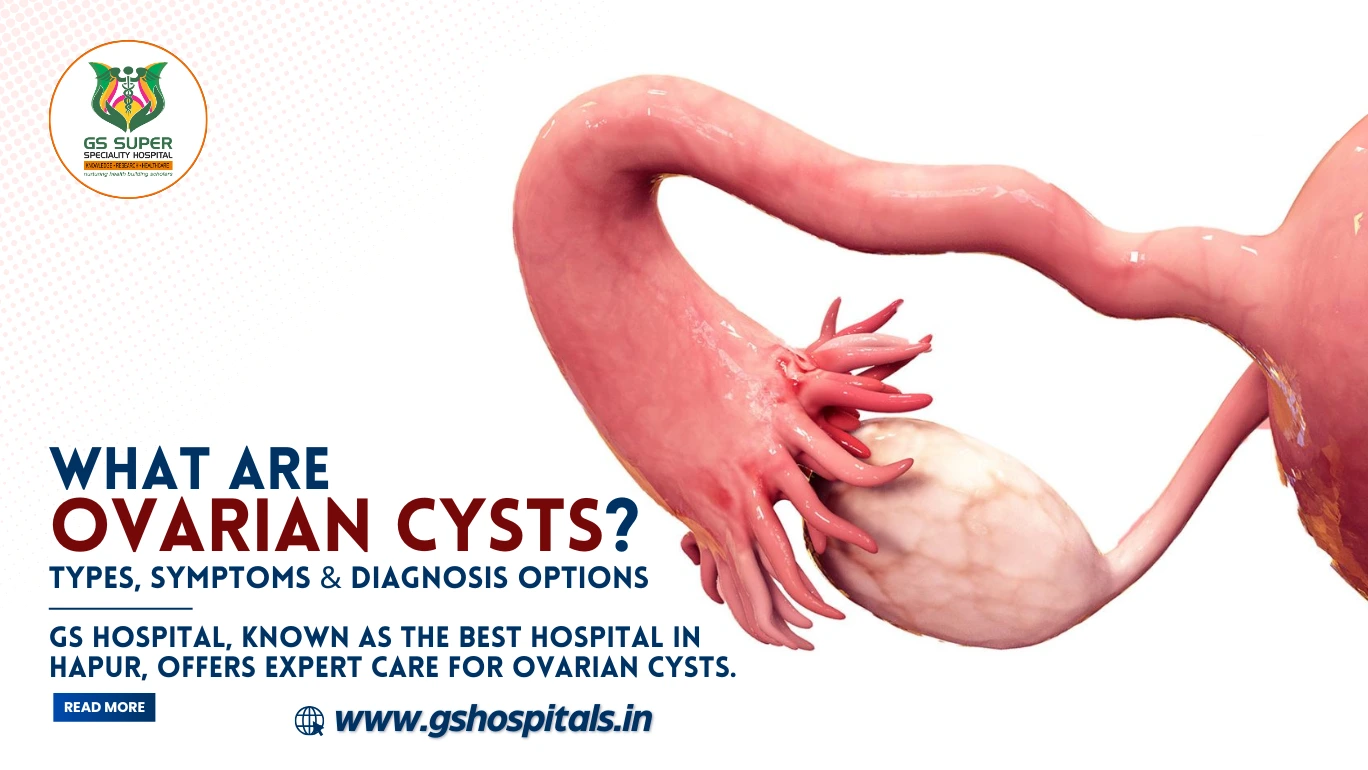
Understanding Ovarian Cysts:
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop either on the surface or inside the ovaries, part of the female reproductive system. While most ovarian cysts are benign (non-cancerous) and may go unnoticed due to a lack of symptoms, some can lead to discomfort or serious complications such as rupture or ovarian torsion.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?:
Ovarian cysts vary in size, content, and type. They can be filled with liquid, semi-solid material, or gas. Common types include:
Functional Cysts:
- These are the most common and form during the menstrual cycle.
- Examples include follicular cysts (formed when the follicle doesn’t release an egg) and corpus luteum cysts (formed after the follicle releases the egg).
Pathological Cysts:
- Caused by abnormal cell growth, these may require medical attention.
- Examples include dermoid cysts, endometriomas, or cystadenomas.
The Role of Ovaries:
The ovaries are critical organs in the female reproductive system, serving dual functions:
Egg Release:
- Ovaries release eggs during ovulation, a key step in reproduction.
Hormone Production:
- They produce essential hormones like estrogen and progesterone that regulate the menstrual cycle and overall reproductive health.
When cysts form, they can interfere with these functions, particularly if they grow excessively large or fail to resolve naturally.
Types of Ovarian Cysts:
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form in or on the ovaries. These cysts are broadly categorized into functional cysts, pathological cysts, and polycystic ovaries, each with unique characteristics and causes. Understanding these types is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment to avoid potential complications.
1. Functional Cysts:
Functional cysts are the most common type and typically form during the menstrual cycle. These cysts are usually harmless and may resolve on their own without medical intervention.
Follicular Cysts:
- Develop when a follicle, which houses a maturing egg, fails to release the egg during ovulation.
- Instead, the follicle swells with fluid, forming a cyst.
- These cysts are often asymptomatic but may cause mild discomfort.
Corpus Luteum Cysts:
- Form after the follicle releases an egg and the remaining structure (corpus luteum) seals itself instead of breaking down.
- These cysts may fill with blood or fluid and sometimes cause symptoms like pain or irregular periods.
2. Pathological Cysts:
Pathological cysts are less common and result from abnormal cell growth. These cysts may require medical treatment or surgical intervention.
Dermoid Cysts (Teratomas):
- Contain tissue such as hair, skin, or teeth due to their origin in embryonic cells.
- These cysts are generally benign but may grow large and cause complications.
Endometriomas:
- Develop when endometrial tissue, typically lining the uterus, grows on the ovary.
- Often associated with endometriosis, they can lead to pelvic pain and fertility issues.
Cystadenomas:
- Arise from the surface tissue of the ovary and may be filled with fluid or mucus.
- While mostly benign, these cysts can grow large and cause discomfort or ovarian torsion.
3. Polycystic Ovaries (PCOS):
Polycystic ovaries contain multiple small cysts due to hormonal imbalances, often associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). This condition may lead to:
- Irregular menstrual cycles.
- Excess androgen levels causing symptoms like acne or excessive hair growth.
- Difficulty conceiving due to disrupted ovulation.
Causes and Risk Factors of Ovarian Cysts:
Ovarian cysts are a common gynecological condition with a variety of causes and risk factors. While most cysts are benign, understanding their origin and associated risks is crucial for prevention and early intervention.
Common Causes of Ovarian Cysts:
Several physiological and pathological factors contribute to the formation of ovarian cysts:
1. Hormonal Imbalances:
- Disruptions in hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone, can lead to the development of functional cysts such as follicular and corpus luteum cysts.
- Hormonal treatments, including fertility drugs, may increase the likelihood of cyst formation.
2. Endometriosis:
- A condition where endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus, often affecting the ovaries.
- This can result in the formation of endometriomas, which are cysts filled with thick, dark fluid.
3. Pregnancy:
- During pregnancy, a corpus luteum cyst may form as the ovary supports early pregnancy through hormone production. These cysts typically resolve on their own but may occasionally cause discomfort.
4. Pelvic Infections:
- Severe infections, particularly those that spread to the ovaries or fallopian tubes, can lead to abscess formation.
- These infections can result in complex cystic structures requiring prompt medical attention.
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cysts:
While ovarian cysts can occur in any woman of reproductive age, certain factors increase the risk:
1. A History of Ovarian Cysts:
- Women who have previously experienced ovarian cysts are at a higher risk of recurrence.
2. Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
- Inconsistent ovulation or hormonal fluctuations associated with irregular cycles may contribute to cyst development.
3. Hormonal Treatments:
- Medications designed to stimulate ovulation, such as fertility drugs, can increase the risk of cyst formation, particularly functional cysts.
4. Endometriosis or PCOS:
- Endometriosis: Women with this condition are more likely to develop endometriomas.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Characterized by multiple small cysts on the ovaries due to hormonal imbalances.
5. Age and Lifestyle Factors:
- Reproductive-age women are more prone to ovarian cysts.
- Factors like obesity and smoking may exacerbate hormonal imbalances, increasing the likelihood of cyst formation.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cysts:
Accurate diagnosis is critical for managing ovarian cysts and preventing potential complications. At GS Hospital, recognized for its team of Top Gynaecologists in Ghaziabad, advanced diagnostic techniques and personalized care are provided to ensure comprehensive assessment and treatment. Diagnostic Methods for Ovarian Cysts:
1. Pelvic Examination:
A pelvic examination is often the first step in diagnosing ovarian cysts.
- Purpose: Detects abnormalities in the ovaries, uterus, or other pelvic structures.
- Process: A manual assessment allows the doctor to identify any swelling or tenderness in the pelvic region.
2. Ultrasound Imaging:
Ultrasound is the primary tool for visualizing ovarian cysts.
Types of Ultrasound:
- Transabdominal Ultrasound: Offers an external view of the ovaries.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Provides a clearer and more detailed image of ovarian structures.
- Benefits: Determines the size, shape, and composition of the cyst, differentiating between solid, fluid-filled, or complex cysts.
3. Blood Tests:
Blood tests help evaluate the nature of the cyst and identify underlying conditions.
CA-125 Test:
- Measures levels of the cancer antigen 125 protein in the blood.
- Useful in detecting ovarian cancer, especially in postmenopausal women or those with suspicious cysts.
Hormonal Tests:
- Identify imbalances, such as those caused by Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
- Assess reproductive hormones like FSH, LH, and estrogen.
4. Advanced Imaging Techniques:
When more detailed visualization is necessary, advanced imaging may be recommended.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
- Provides a detailed view of ovarian tissues and surrounding structures.
- Useful for complex or suspicious cysts.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan:
- Helps in evaluating larger cysts or those affecting adjacent organs.
5. Laparoscopy:
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure for both diagnosis and treatment.
Procedure:
- Involves making a small incision and inserting a thin tube with a camera.
- Allows direct visualization of the ovaries and other pelvic organs.
Benefits:
- Confirms the diagnosis with a direct view.
- Enables immediate treatment, such as cyst removal, if necessary.
Treatment Options for Ovarian Cysts:
The treatment for ovarian cysts varies based on their size, type, and associated symptoms. At GS Hospital, the approach is patient-centered, ensuring both immediate relief and long-term health. Below are the key treatment strategies:
1. Watchful Waiting:
For small, simple cysts that are asymptomatic and unlikely to cause complications, a conservative approach is often recommended.
What It Involves:
- Regular ultrasounds to monitor the cyst for growth or changes.
- Periodic check-ups to ensure there are no new symptoms or complications.
When It’s Suitable:
- Functional cysts such as follicular or corpus luteum cysts that often resolve on their own.
- Patients with no significant pain or disruption in daily life.
2. Medications:
Medications are prescribed to manage symptoms or prevent the recurrence of cysts.
Hormonal Birth Control:
Purpose:
- Regulates menstrual cycles, reducing the likelihood of new cysts forming.
- Prevents the growth of existing functional cysts.
- Forms: Pills, patches, or intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Pain Relievers:
- Use: Provides relief from pelvic discomfort or pain caused by cysts.
- Common Options: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or prescription-strength drugs for severe pain.
3. Surgical Intervention:
When cysts are large, persistent, symptomatic, or suspected to be malignant, surgery becomes necessary.
Laparoscopy:
Procedure:
- Minimally invasive surgery performed through small incisions.
- Suitable for removing small, non-cancerous cysts.
Advantages:
- Faster recovery.
- Minimal scarring.
Laparotomy:
Procedure:
- Open surgery used for larger cysts or those suspected to be cancerous.
- Provides a thorough examination and removal of cysts or affected ovaries if needed.
When It’s Recommended:
- Large, complex cysts.
- Cases where cancer cannot be ruled out.
4. Treatment for Underlying Conditions:
Addressing root causes is vital for preventing recurrence.
PCOS Management:
- Lifestyle changes, medications, or hormonal treatments to regulate ovulation and reduce cyst formation.
Endometriosis Treatment:
- Surgical removal of endometrial tissue.
- Hormonal therapies to prevent future growth.
Why Choose GS Hospital?:
GS Hospital, a leading healthcare institution in Uttar Pradesh, is renowned for its exceptional gynecological and obstetric care. With a commitment to excellence, cutting-edge technology, and compassionate service, it stands as a trusted choice for patients seeking comprehensive reproductive healthcare. Key Features of GS Hospital:
1. Expert Team of Specialists:
GS Hospital is home to some of the Best Gynaecologist in Meerut UP and Ghaziabad, bringing years of experience and expertise in diagnosing and treating a wide range of gynecological conditions.
- Highly qualified gynecologists and obstetricians with national and international credentials.
- A multidisciplinary team approach for managing complex cases, including collaboration with radiologists, oncologists, and fertility specialists.
2. Advanced Diagnostic and Surgical Facilities:
The hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art technology to ensure accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
Diagnostic Tools:
- High-resolution ultrasound machines for detailed imaging.
- Hormonal testing and advanced screening for conditions like PCOS and endometriosis.
- Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy for minimally invasive diagnosis and treatment.
Surgical Expertise:
- Procedures ranging from routine gynecological surgeries to complex oncological treatments.
- Minimally invasive techniques that reduce recovery time and complications.
3. Personalized Patient Care:
Every patient at GS Hospital receives individualized attention and treatment plans tailored to their unique needs.
- Comprehensive consultation to address patient concerns.
- Customized treatment options, whether for ovarian cysts, fertility issues, or high-risk pregnancies.
- Continuous support and follow-up to ensure optimal health outcomes.
4. Focus on Patient Education and Preventive Care:
GS Hospital places a strong emphasis on empowering patients with knowledge about their health.
- Educational workshops on reproductive health, pregnancy care, and menopause management.
- Guidance on preventive measures, such as regular check-ups and lifestyle changes, to reduce the risk of gynecological issues.
- Detailed explanations of treatment plans to ensure patients make informed decisions.
5. Additional Benefits of Choosing GS Hospital:
- Compassionate Care: The staff is dedicated to providing a welcoming and supportive environment for all patients.
- Accessibility: Conveniently located for patients in Meerut, Ghaziabad, and surrounding areas.
- Comprehensive Services: A one-stop destination for gynecology, obstetrics, infertility treatments, and cancer care.
Conclusion
Ovarian cysts are a common yet often misunderstood condition. By understanding their types, symptoms, and diagnosis options, women can take proactive steps toward maintaining their reproductive health.
At GS Hospital, patients receive comprehensive care from the Best Gynaecologists and Obstetricians in Ghaziabad and Meerut UP. Whether you need routine check-ups, diagnostic tests, or advanced treatment, GS Hospital is here to support you every step of the way.
FAQs
1. What makes GS Hospital the Best Hospital in Hapur for ovarian cyst treatment?
GS Hospital combines advanced diagnostic tools, experienced gynaecologists, and compassionate care to provide exceptional treatment for ovarian cysts.
2. Are ovarian cysts always harmful?
No, most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve on their own. However, some can cause complications and require treatment.
3. When should I see a doctor for ovarian cysts?
Seek medical attention if you experience severe abdominal pain, bloating, or irregular periods. Regular check-ups are also recommended for early detection.
4. Can ovarian cysts affect fertility?
Certain cysts, such as those caused by PCOS or endometriosis, can impact fertility. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
5. Does GS Hospital provide minimally invasive surgery for ovarian cysts?
Yes, GS Hospital specializes in laparoscopic surgery, a minimally invasive option for removing cysts with faster recovery times.
