How to Give Quality Treatment to Heart Attack Patient Immediately
Published On : July 25, 2024
A heart attack is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention and intervention. Knowing how to provide quality treatment to a heart attack patient can save lives and reduce long-term damage. This article will guide you through the steps necessary to handle such an emergency effectively. We will also discuss the role of GS Hospital, recognized as the best heart care centre in Ghaziabad and Meerut, in providing top-notch heart care services.
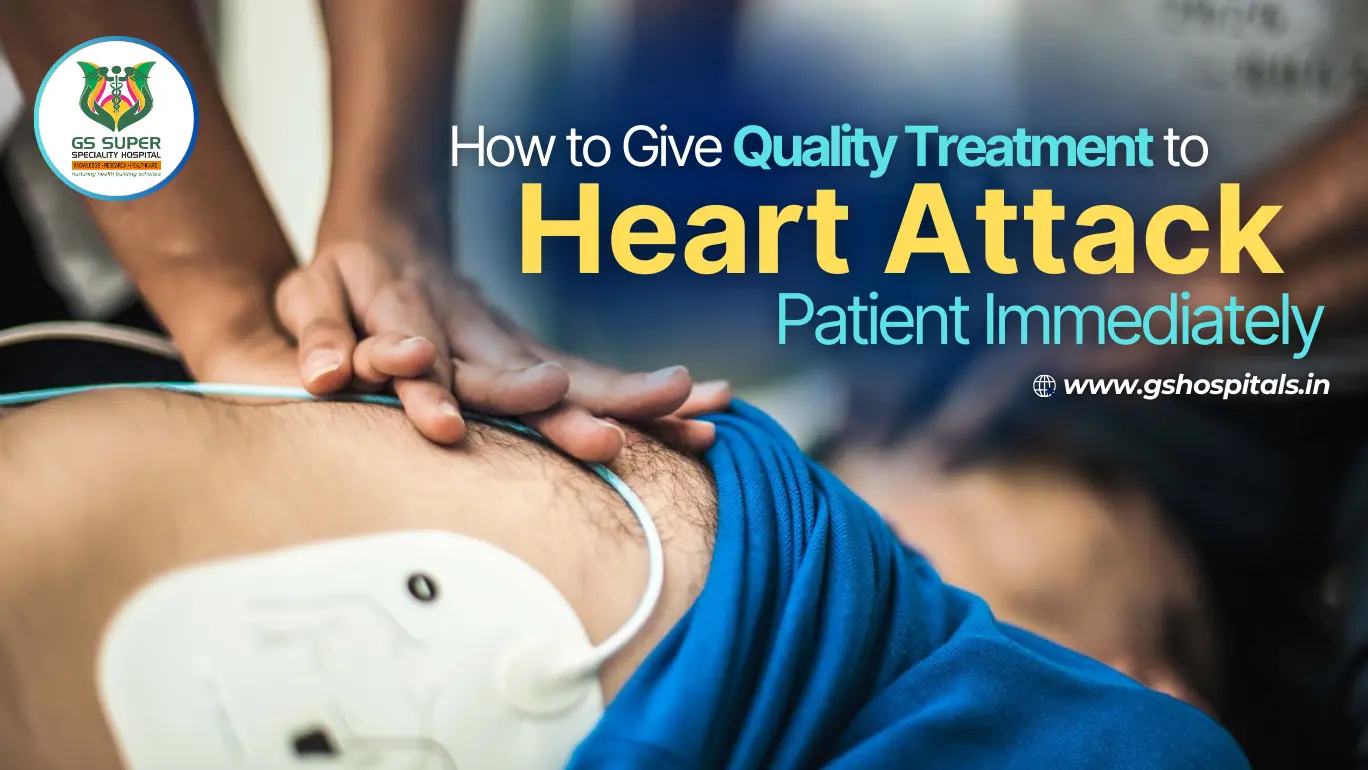
Understanding Heart Attacks:
A heart attack, medically known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked long enough for part of the heart muscle to be damaged or die. This blockage is most commonly caused by the buildup of plaque in one or more coronary arteries.
Causes and Risks:
- Plaque Buildup: Leads to narrowed arteries and restricted blood flow.
- Risk Factors: Include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle.
The Role of Immediate Treatment:
Prompt treatment is critical in reducing heart muscle damage and increasing survival chances. The first few minutes following a heart attack are vital in determining the patient's outcome.
Immediate Response:
- Emergency Medical Services: Call for help immediately.
- First Aid: Administer aspirin if advised and perform CPR if necessary.
- Advanced Medical Interventions: Angioplasty, medications, or surgery may be required.
GS Hospital: Leading Heart Care Provider:
GS Hospital in Ghaziabad is renowned for its exceptional heart care services. Recognized as one of the top heart care hospital in UP, it boasts advanced technology and a team of experienced cardiologists.
Key Features:
- State-of-the-Art Technology: Equipped with the latest medical advancements for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Experienced Cardiologists: Highly skilled in managing complex heart conditions.
- Comprehensive Care: Provides a full spectrum of heart care services, from emergency interventions to rehabilitation.
By understanding the importance of immediate treatment and choosing a leading heart care provider like GS Hospital, patients can significantly improve their chances of a positive outcome following a heart attack.
Using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED):
Importance of AED:
An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a crucial tool in emergencies involving sudden cardiac arrest. It can restore a normal heart rhythm by delivering an electric shock to the heart. AEDs are user-friendly and designed to be operated by laypeople with minimal training, making them accessible in public places and workplaces.
How to Use an AED:
1. Turn on the AED:
- Activation: Power on the AED by pressing the indicated button. Follow the voice and visual prompts provided by the device.
2. Attach the Pads:
- Pad Placement: Place the adhesive pads on the patient’s bare chest according to the diagram on the pads. One pad should be placed on the upper right side of the chest, and the other on the lower left side.
3. Analyze the Rhythm:
- Safety Check: Ensure that no one is touching the patient while the AED analyzes the heart rhythm. This step is critical to get an accurate reading and avoid interference.
4. Deliver the Shock:
- Shock Administration: If the AED advises a shock, make sure everyone is clear and press the shock button when prompted. The AED will administer the shock to restore a normal heart rhythm.
- Resume CPR: Immediately resume CPR after the shock. Continue with chest compressions and rescue breaths as needed.
Additional Tips:
- Follow Instructions: Adhere strictly to the AED’s voice prompts throughout the process.
- Ensure Proper Contact: Make sure the pads have good contact with the patient’s skin and are not obstructed by clothing or medical devices.
- Seek Professional Help: Continue using the AED and performing CPR until emergency medical services arrive or the patient shows signs of life.
- By following these steps, you can effectively use an AED to help save a life in the event of sudden cardiac arrest.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Heart Attack:
Common Symptoms:
Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack early can be life-saving. The most frequent symptoms include:
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: Often described as a squeezing, pressure, or fullness in the chest.
- Shortness of Breath: May occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some patients feel nauseated or vomit.
- Pain in Other Areas: Discomfort in one or both arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
Less Common Symptoms:
Some symptoms are less typical but equally important to recognize:
- Cold Sweat: Sudden sweating without an apparent reason.
- Lightheadedness: Feeling dizzy or lightheaded.
- Fatigue: Unusual tiredness or fatigue.
Additional Signs to Watch For:
Being aware of all possible symptoms can help ensure prompt medical attention:
- Upper Body Discomfort: Pain that spreads to the shoulders or upper back.
- Indigestion: Some people may mistake heart attack symptoms for indigestion or heartburn.
- Anxiety: A feeling of impending doom or severe anxiety can sometimes accompany a heart attack.
By understanding and recognizing both common and less common symptoms, individuals can act quickly to seek emergency medical care, potentially saving lives.
Immediate Steps to Take During a Heart Attack:
Call for Emergency Help:
The first and most crucial step is to call emergency services immediately. In India, dial 108 for an ambulance to ensure professional medical assistance is on the way.
Administer Aspirin:
Aspirin helps prevent blood clotting and can reduce the severity of a heart attack. If the patient is not allergic, have them chew and swallow a 325 mg aspirin tablet.
Perform CPR if Necessary:
If the patient is unconscious and not breathing, initiate CPR. Push hard and fast in the center of the chest at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute.
Use an AED if Available:
An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) can be crucial if the heart has stopped. Follow the device instructions carefully to administer a shock and potentially restart the heart.
Additional Tips:
- Stay Calm: Keep the patient as calm and comfortable as possible.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep a close watch on the patient’s symptoms and be ready to provide updates to emergency responders.
- Avoid Food and Drink: Do not give the patient anything to eat or drink.
By following these immediate steps, you can significantly improve the patient's chances of survival and reduce the potential damage to their heart.
Administering CPR:
When to Perform CPR:
CPR should be initiated immediately if the patient is unresponsive and not breathing. This emergency procedure can help maintain circulation and oxygenation, buying crucial time until professional medical help arrives.
How to Perform CPR:
Position Your Hands:
- Hand Placement: Place the heel of one hand on the center of the patient’s chest. Place your other hand on top, interlocking your fingers.
- Body Position: Position yourself directly over the patient's chest to use your body weight effectively for compressions.
Perform Chest Compressions:
- Compression Technique: Push hard and fast on the center of the chest.
- Rate and Depth: Aim for a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. Compress the chest to a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) for adults, allowing the chest to recoil completely between compressions.
Rescue Breaths:
- When to Give Breaths: If you are trained in CPR and comfortable providing rescue breaths, give two breaths after every 30 compressions.
- Technique: Tilt the patient’s head back slightly to open the airway, lift the chin, and pinch the nose shut. Give two slow breaths, each lasting about 1 second, ensuring the chest rises with each breath.
Additional Tips:
- Continue CPR: Do not stop CPR until emergency medical personnel take over or the patient starts to show signs of life.
- Automated External Defibrillator (AED): If an AED is available, use it as soon as possible, following the device’s instructions.
By following these steps, you can effectively perform CPR, significantly increasing the patient’s chances of survival in a cardiac emergency.
In the Hospital: Initial Treatment for a Heart Attack:
Electrocardiogram (ECG):
Upon arrival at the hospital, an ECG is performed to assess the severity and location of the heart attack. This diagnostic tool is crucial for guiding the treatment plan.
Medications:
Several medications are administered to manage a heart attack effectively:
- Thrombolytics: These drugs dissolve blood clots.
- Antiplatelet Agents: Prevent new clots from forming.
- Beta-Blockers: Reduce the heart’s workload.
- ACE Inhibitors: Help relax blood vessels.
Angioplasty and Stenting:
In some cases, angioplasty is performed to open blocked arteries. During this procedure, a stent may be placed to keep the artery open and ensure proper blood flow.
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery:
For severe blockages, coronary artery bypass surgery might be necessary. This procedure involves creating a new pathway for blood to flow to the heart, bypassing the blocked arteries.
Additional Interventions:
- Continuous Monitoring: Vital signs and heart function are closely monitored.
- Pain Management: Medications are given to manage chest pain and discomfort.
- Rehabilitation Planning: Post-treatment, a rehabilitation plan is developed to support recovery and prevent future heart issues.
By following these initial treatments and interventions, hospitals aim to stabilize the patient, minimize heart damage, and set the stage for long-term recovery.
GS Hospital’s Approach to Heart Attack Treatment:
State-of-the-Art Facilities:
The best Hospital in Meerut like GS Hospital is equipped with the latest technology for diagnosing and treating heart conditions. Renowned as one of the best hospital in Hapur and Meerut for heart care, it offers advanced facilities to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Experienced Cardiologists:
The hospital boasts a team of highly skilled and experienced cardiologists who provide personalized care to each patient. These experts are well-versed in the latest treatment protocols and dedicated to delivering the highest standard of care.
Comprehensive Care:
GS Hospital offers a full spectrum of care for heart attack patients, from emergency treatment to rehabilitation:
- Emergency Services: Rapid response and immediate treatment to minimize heart damage.
- Diagnostic Services: Advanced imaging and testing to accurately assess the condition.
- Rehabilitation Programs: Customized plans to support recovery and prevent future heart issues.
Patient-Centered Approach:
GS Hospital emphasizes compassionate care, ensuring that patients and their families are well-informed and comfortable throughout the treatment process. The hospital prioritizes:
- Patient Education: Clear communication about the treatment plan and recovery process.
- Emotional Support: Providing a supportive environment for both patients and their families.
- Comfort and Convenience: Ensuring a comfortable stay with all necessary amenities.
By combining advanced technology, expert care, and a patient-centered approach, GS Hospital delivers exceptional heart attack treatment and supports patients on their journey to recovery.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes:
Diet and Nutrition:
Adopting a healthy diet is crucial for heart health:
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit Unhealthy Fats: Reduce intake of saturated and trans fats found in processed and fried foods.
- Monitor Cholesterol Levels: Maintain healthy cholesterol levels with a balanced diet rich in fiber and low in unhealthy fats.
Exercise:
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health:
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, most days of the week.
- Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week to improve muscle mass, metabolism, and overall health.
Avoid Smoking:
Quitting smoking is one of the most significant steps you can take to improve heart health. Smoking cessation reduces the risk of heart disease, improves lung function, and enhances overall well-being.
Regular Check-Ups:
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are vital for monitoring and managing risk factors for heart disease. These appointments help in:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and addressing potential heart disease risks early.
- Health Monitoring: Keeping track of blood pressure, cholesterol, and glucose levels.
- Preventive Care: Receiving guidance on lifestyle changes and preventive measures.
By implementing these preventive measures and lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and promote long-term heart health. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, smoking cessation, and consistent medical check-ups are key components of a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion
Providing quality treatment to a heart attack patient immediately can save lives and reduce long-term damage. Recognizing the symptoms and taking prompt action is crucial. GS Hospital, with its state-of-the-art facilities and experienced cardiologists, is a Top Heart Care Hospital in Ghaziabad. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can help ensure the best possible outcome for a heart attack patient.
FAQs
1. What are the first signs of a heart attack?
The first signs of a heart attack often include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea, and pain in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
2. What should I do if I think someone is having a heart attack?
Call emergency services immediately, administer aspirin if the person is not allergic, and start CPR if the person is unconscious and not breathing.
3. Can a heart attack be treated at home?
No, a heart attack requires immediate medical attention. While waiting for emergency services, you can administer aspirin and perform CPR if necessary.
4. What makes GS Hospital a top choice for heart care?
GS Hospital is equipped with advanced technology and a team of experienced cardiologists, providing comprehensive and compassionate care for heart attack patients.
5. How can I reduce my risk of having a heart attack?
You can reduce your risk by maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, and having regular check-ups with your healthcare provider.
