Blood Clot in Brain: Types, Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Published On : November 14, 2024
A blood clot in the brain, known as cerebral thrombosis or cerebral embolism, is a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention. Blood clots can restrict or block blood flow to essential areas of the brain, leading to strokes and other complications. At GS Hospital, one of the best neuro hospital in Ghaziabad and among the top 10 private hospitals in Uttar Pradesh, we have a dedicated team specializing in the treatment and management of neurological conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the types, symptoms, causes, and treatments for brain clots, offering insights into how early diagnosis and prompt care can make all the difference.
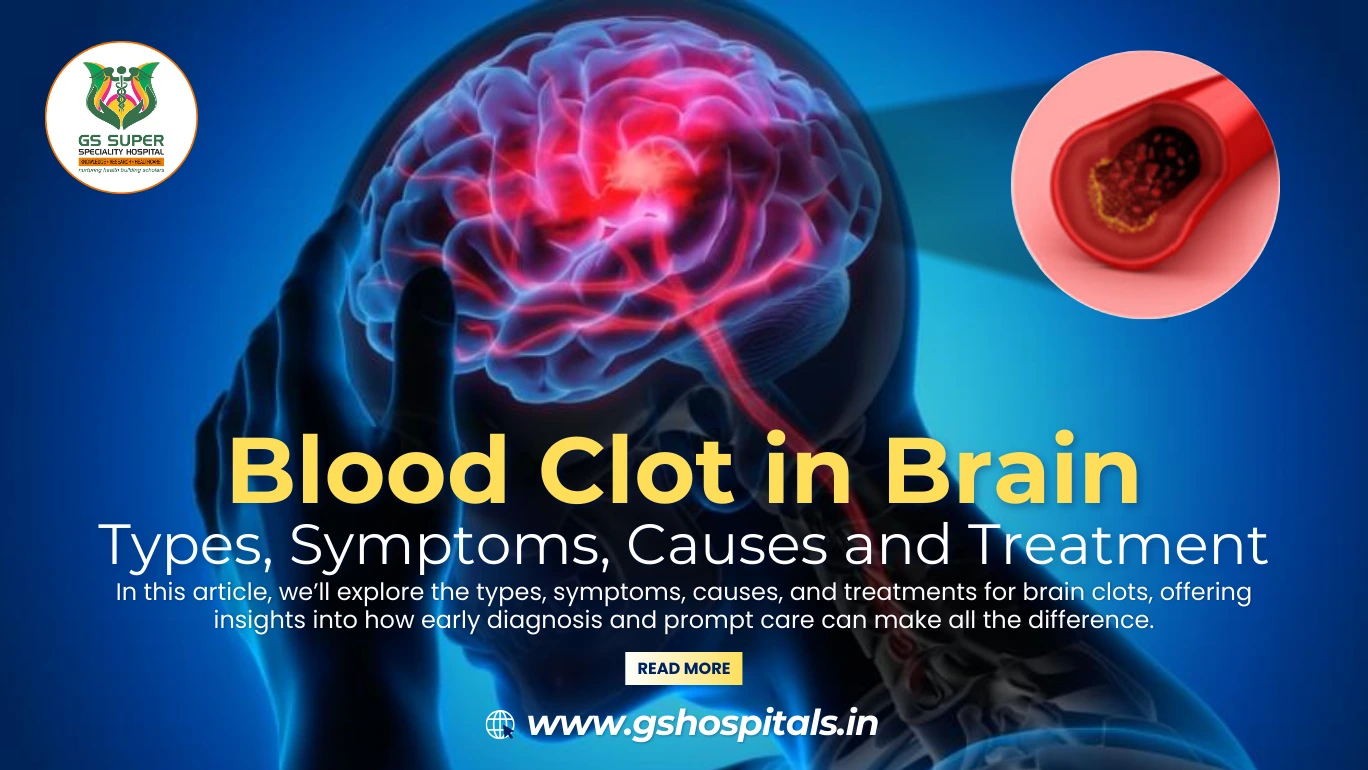
Understanding a Blood Clot in the Brain:
A blood clot in the brain occurs when a blockage forms in a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of oxygen-rich blood to brain tissue. This interruption in blood supply causes brain cells to quickly become deprived of oxygen and nutrients, leading to cell death and severe neurological symptoms. Blood clots in the brain are a leading cause of stroke, which is a critical medical emergency that can result in lasting brain damage or even be fatal if not treated promptly.
Key Points on Blood Clots in the Brain:
- What Happens: The blockage restricts oxygen and nutrient flow to the brain, leading to cell death.
- Symptoms: Patients may experience sudden headaches, vision changes, confusion, dizziness, and weakness, often on one side of the body.
- Stroke Risk: Blood clots are a major cause of ischemic stroke, which requires immediate medical attention to prevent severe consequences.
- Types of Clots: Clots may develop within the brain’s arteries or can travel from other parts of the body, like the heart or legs, to lodge in brain vessels.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Health Conditions: High blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, and high cholesterol increase clot risks.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to clot formation.
- Genetics and Age: Family history and advanced age also raise the likelihood of blood clots in the brain.
Immediate Medical Attention Needed:
If you suspect a blood clot in the brain, seek medical care urgently. Early intervention can prevent further brain damage and improve recovery outcomes.
Types of Blood Clots in the Brain:
Blood clots in the brain can lead to serious medical emergencies, primarily taking the form of two main types of stroke: Ischemic Stroke and Hemorrhagic Stroke. Each has distinct causes, mechanisms, and treatment approaches.
1. Ischemic Stroke: Blockage of Blood Flow:
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms within a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain, obstructing blood flow and depriving brain cells of oxygen.
Causes:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of fatty deposits (plaques) within the blood vessels narrows the arteries, increasing the risk of a clot forming.
- Blood Clot Formation: Blood clots can develop in narrowed areas or as a result of other health issues such as irregular heart rhythms (atrial fibrillation).
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, poor diet, and lack of physical activity can contribute to the buildup of plaque and increase ischemic stroke risk.
2. Hemorrhagic Stroke: Bleeding in the Brain:
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding and pressure buildup that can damage brain tissue.
Causes:
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension puts stress on blood vessel walls, increasing the risk of rupture.
- Aneurysms: Weak spots in blood vessels can balloon and burst under pressure.
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): Abnormal connections between arteries and veins can lead to vessel rupture.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical impact can also lead to bleeding within the brain.
Recognizing Symptoms of a Blood Clot in the Brain:
Blood clots in the brain, often associated with strokes, present symptoms that vary based on the clot’s location and severity. These symptoms can be sudden and life-threatening, so recognizing them quickly is crucial for timely medical intervention. Here are common signs to watch for and what they may indicate:
1. Sudden Weakness or Numbness:
- One-Sided Symptoms: Often, blood clots in the brain affect one side of the body, causing weakness or numbness in areas such as the face, arm, or leg.
- Facial Drooping: This can manifest as an uneven smile or difficulty moving one side of the face.
- Arm Weakness: Affected individuals may find it challenging to raise one arm or keep it lifted without it drifting downwards.
- Leg Numbness: Walking or standing may become difficult or unsteady.
2. Speech Difficulties:
- Slurred Speech: People with a blood clot in the brain may struggle to pronounce words, resulting in slurred or garbled speech.
- Inability to Form Words: Clots impacting certain brain areas can interfere with the ability to form coherent sentences.
- Difficulty Understanding Speech: Beyond speaking issues, some may find it hard to comprehend what others are saying, leading to confusion in conversation.
3. Vision Problems:
- Sudden Vision Loss: This may occur in one or both eyes, often described as a "curtain" falling over the vision.
- Blurred or Double Vision: Blood clots can disrupt normal eye coordination, causing double vision or blurriness.
- Partial Vision Loss: Some individuals may lose vision in part of their visual field, often without realizing it immediately.
4. Severe Headache:
- Thunderclap Headache: Described as a sudden and extremely painful headache, this symptom can signal a hemorrhagic stroke, where bleeding in the brain increases intracranial pressure.
- Unusual or Unfamiliar Pain: Unlike common headaches, these may feel sharp, intense, and escalate quickly.
- Accompanying Symptoms: These headaches are often accompanied by other signs like neck stiffness, nausea, or vomiting, especially if bleeding is involved.
5. Dizziness or Loss of Balance:
- Sudden Dizziness: Blood clots may disrupt blood flow to areas responsible for balance, leading to sudden and unexplained dizziness.
- Loss of Coordination: People may find it challenging to walk straight or stay upright.
- Unsteady Gait: An uncoordinated or “staggering” walk may signal a clot impacting brain regions that control motor skills.
6. Confusion and Cognitive Issues:
- Trouble Understanding: Patients might appear confused, struggle with comprehension, or have difficulty following simple instructions.
- Disorientation: This includes being unsure of time, place, or identity, especially if the clot affects areas related to memory and cognition.
- Sudden Memory Lapses: Clots that affect the brain’s memory centers can cause sudden forgetfulness or confusion about familiar people or surroundings.
Urgency of Seeking Medical Attention:
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it is critical to seek medical help immediately. Blood clots in the brain require rapid response to minimize brain damage and increase the chances of recovery. Swift treatment, including clot-dissolving medications and other interventions, can be lifesaving.
Diagnosis of Blood Clots in the Brain:
Accurate and rapid diagnosis is essential when a blood clot is suspected in the brain. Proper identification of a clot can prevent further complications and facilitate timely, targeted treatment. The Top 10 private hospitals in Uttar Pradesh like GS Hospital, our specialists employ advanced diagnostic techniques to detect brain clots with precision and efficiency. Here are the primary methods used:
1. CT Scan:
- Rapid Imaging: CT scans are often the first step, as they can quickly reveal bleeding, blockages, or abnormalities within the brain.
- Stroke Detection: This scan helps determine if the stroke is ischemic (caused by a clot) or hemorrhagic (caused by bleeding).
- Guides Initial Treatment: The results can help doctors make immediate decisions about initial treatment steps.
2. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
- Detailed Visualization: MRIs produce high-resolution images, allowing for a closer look at smaller clots or damaged areas.
- Distinguishes Between Tissues: MRI can reveal more subtle signs of injury, making it useful for understanding the extent of brain tissue damage.
- Ideal for Complex Cases: MRI is often used when CT scans are inconclusive or when further detail is needed.
3. Doppler Ultrasound:
- Blood Flow Assessment: This non-invasive test measures blood flow through the arteries in the neck and brain.
- Detects Blockages: Doppler ultrasound can indicate blockages or narrowed arteries, which are risk factors for clots.
- Portable Option: It is especially valuable for ongoing monitoring or when quick bedside assessments are needed.
4. Angiography:
- Blood Vessel Visualization: Angiography involves injecting a contrast dye to make blood vessels visible on X-ray images.
- Identifies Precise Blockage Location: It provides a clear map of the arteries and pinpoints the clot’s exact location.
- Useful in Planning Surgery: Angiography helps neurosurgeons plan procedures by giving a clear view of the vascular structure.
Treatment Options for Blood Clots in the Brain:
Treating brain clots depends on the type of stroke and the severity of the condition. The top 10 Best Neurology Hospitals in Uttar Pradesh like GS Hospital offers a range of treatment options to manage blood clots effectively:
1. Medications:
- Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners): Medications such as warfarin or heparin prevent further clot formation and help reduce the risk of additional strokes.
- Thrombolytics (Clot-Busting Drugs): These medications dissolve existing clots and are highly effective if administered within hours of symptom onset.
- Anti-Platelet Drugs: Medications like aspirin may be prescribed to prevent platelets from sticking together and forming new clots.
2. Surgical Intervention:
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: In this minimally invasive procedure, a catheter is used to physically remove the clot from the blocked blood vessel, often through a tiny incision.
- Craniotomy: For hemorrhagic strokes, a craniotomy may be necessary to relieve pressure caused by bleeding in the brain.
- Endovascular Procedures: These involve inserting devices to treat blood vessel issues, such as stents to keep arteries open.
3. Physical Rehabilitation:
- Physical Therapy: Helps patients rebuild strength and mobility that may be lost due to stroke-related damage.
- Occupational Therapy: Assists patients in relearning daily activities and improving fine motor skills.
- Speech and Cognitive Therapy: Restores language and cognitive abilities affected by the clot’s impact on brain function.
Preventing Blood Clots in the Brain:
Preventing brain clots involves lifestyle adjustments and medical management to reduce the risk of clots forming. Here are some effective steps:
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet:
- Focus on Heart-Healthy Foods: A diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins supports cardiovascular health.
- Limit Saturated Fats and Sugars: Reducing these can help lower cholesterol and blood pressure, both of which are risk factors for clots.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Fiber helps manage cholesterol, which can reduce plaque buildup in blood vessels.
2. Engage in Regular Exercise:
- Boost Circulation: Physical activity improves blood flow and reduces the risk of clots.
- Promotes Heart Health: Regular exercise supports a healthy heart and vascular system.
- Reduces Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce strain on blood vessels and lower clot risk.
3. Quit Smoking:
- Improves Vascular Health: Smoking damages blood vessels and raises the risk of clot formation.
- Reduces Stroke Risk: Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to lower the likelihood of both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
- Improves Overall Health: Reducing or eliminating tobacco use has numerous long-term health benefits.
4. Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol:
- Monitor Regularly: Regular check-ups allow for early detection and management of high blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Medication Adherence: If prescribed, take blood pressure or cholesterol medications as directed to maintain optimal levels.
- Diet and Lifestyle Support: Reducing salt intake and exercising regularly are also effective in managing blood pressure.
5. Control Diabetes:
- Maintain Stable Blood Sugar Levels: Managing blood sugar through diet, exercise, and medication can help protect blood vessels.
- Regular Monitoring: Consistent monitoring of glucose levels helps prevent complications that may increase clot risk.
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: Lifestyle adjustments that support blood sugar control can also improve overall vascular health.
Conclusion
A blood clot in the brain is a critical medical condition requiring immediate care. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this health risk. At GS Hospital, we pride ourselves on being among the best Neurosurgery Hospitals in UP, providing top-tier care with a dedicated team of neuro specialists ready to assist in emergencies.
For any concerns or if you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms, reach out to GS Hospital a trusted choice in neurology and neurosurgery care. With our expert team and state-of-the-art technology, we’re committed to helping you on your path to recovery and health.
FAQs
1. What are the early signs of a blood clot in the brain?
Sudden weakness, speech difficulties, and severe headache are common early signs.
2. Is a brain clot the same as a stroke?
Yes, a blood clot in the brain can lead to an ischemic stroke, which is a type of stroke.
3. Can a brain clot dissolve on its own?
While some clots may dissolve, immediate medical treatment is essential to avoid serious complications.
4. What should I do if I suspect a blood clot in my brain?
Seek emergency medical attention immediately to prevent potential damage.
5. How does GS Hospital treat blood clots in the brain?
GS Hospital offers comprehensive care with advanced diagnostic tools and treatment options, including medications and minimally invasive surgeries.
